The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved on Monday Opzelura (ruxolitinib) cream 1.5 percent as the topical treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo for adult and pediatrics patients 12 years of age and older.
The approval based on TRuE-V clinical trials applied on more than 600 patients that randomly assigned to Opzelura or placebo among 24 weeks.
After the definite period, the results show that 30 percent of patients who treated with Opzelura achieved about 75 percent improvement from baseline in the facial Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (F-VASI75), while 8-13 percent of patients treated with placebo.
The new medical treatment may take around to 24 weeks to show its effectiveness, which half of Opzelura treated patients achieved F-VASI75 at week 52.
The cream has approved for continuous topical use twice daily to affected areas of up to 10 percent of body surface area in patients.
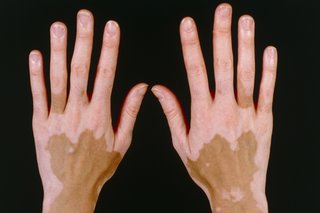
Vitiligo is a long-term condition where pale white patches develop on the skin. It happened in order of the lack of melanin, which called the pigment in skin.
Vitiligo can affect any area of skin, but it commonly happens on the face, neck and hands.
