“We worry a global sudden stop in financing is beginning to emerge, with coronavirus (COVID-19) the underlying driver,” the Institute of International Finance (IIF) is alarmed.
IIF added that the monetary and fiscal easing measures are a welcome palliative, but at the end only a concerted response in terms of testing and containment will be able to mitigate the fear factor in markets and jump-start global demand.
The world currently suffers from a state of terror due to the outbreak of the COVID-19.
Investors have pulled almost $42 billion from developing nations since the coronavirus outbreak began to rattle global markets on Jan. 21, according to data from the IIF. The outflow fueled a 22 percentslump in MSCI Inc.’s emerging-market stock gauge over the same period and pushed down Russia’s ruble and the Colombian and Mexican pesos by at least 15 percent.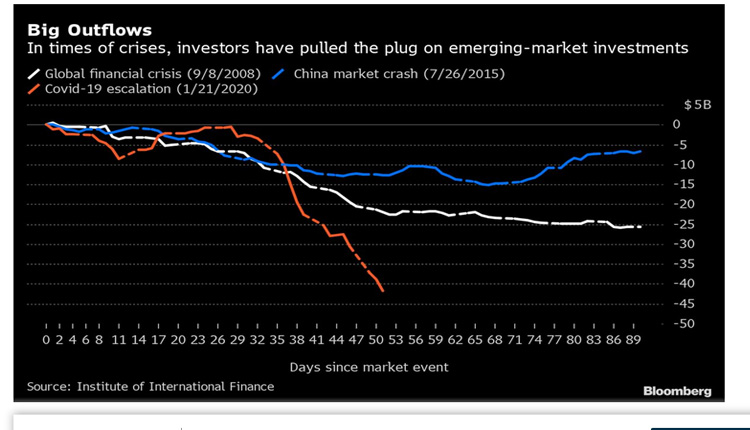
“Our high frequency tracking of non-resident portfolio flows to emerging markets (EM) is a useful gauge of risk appetite and points to a large ‘sudden stop’ on that front as well,” the IIF said.
The IIF expressed its fear for 2020 to be another challenging year for growth across EM.
In terms of the non-resident portfolio flows to EM, the IIF said that its tracker is currently the most negative ever, with outflows exceeding the 2013 “taper tantrum” and the 2008 global financial crisis.
“On an aggregated quarterly basis, flows to China have remained positive, obscuring what is quite a negative picture elsewhere,” the IIF mentioned.
“If we take this flow picture as a possible representation for what is happening to risk assets more broadly, a global ‘sudden stop’ is in the making, one that could present substantial downside risk to our forecasts,” the IIF said in a disappointing tone.
It said that what worries especially is that a decade of extraordinary monetary policy stimulus has by design steered lots of flows into high beta assets, including emerging markets.
The IIF pointed out to that Turkey and Argentina showed in 2018 just how negative “sudden stops” can be for economic activity, with the reversal in foreign financing leading to a shut down in investment from which both countries have yet to recover.
Also, the IIF also cut its US forecast, with the economy flat lining in 2Q as the potential brunt of the COVID-19 shock hits.
It mentioned that the sharp drop in oil prices since then has changed the landscape, raising the risk of credit stress in the US and moving its US forecast closer to recession territory.
“We worry that the unfolding ‘sudden stop’ now has a similar potential, just on a more global and systemic level. We have documented negative growth momentum in many emerging markets even before the COVID-19 shock, including in Mexico and South Africa, so that the initial conditions in many places are weak and vulnerability to a persistent pull-back in foreign financing material,” the IIF concluded.
Risks are mounting for another challenging year for developing nations, as annual average growth in China, where the virus first emerged, probably coming in at 4% rather than the previously expected 6% for 2020, according to the IIF. Global growth could approach 1% in 2020, which would be the weakest pace since 2009, according to the economists
